Foundation Imagine PWS Verslag
<accesscontrol>Imagine</accesscontrol>
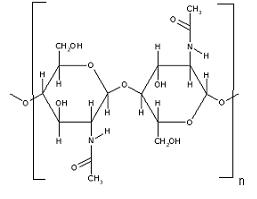
Chitin
What is chitin?
Chitin is a polymer. It is a fiber found in the shells of crustaceans (such as lobsters, crabs and shrimps) and insects. After cellulose, chitin is the most common polysaccharide found in nature. It's physical state is solid. It's color can vary from white to brown or orange depending on the source of the chitin. Chitin is insoluble in most solvents. Chitin does dissolve in concentrated HCI, H2S04, H3P04 and water free HCOOH solutions
Occurrence and availability of chitin
Chitin occurs widely in nature, especially in lower animals – such as spiders, insects and beetles – and fungi, but the exoskeleton of crabs, lobsters and shrimps are also a source of raw material for chitin production (the dry exoskeletons contain from 20 to 50% chitin). The chitin acts as a carbohydrate and nitrogen reserve in the animals.
The arthropod cuticle structure can be considered a two-layer structure of chitin protein complexes. The exocuticle is hardened by polymerization of the proteins with polyphenols and admixed with calcium salts. Chitin occurs mostly in gut linings, tracheae, and wing coverings. As far as the cuticle is concerned, chitin is accompanied by the before mentioned proteins and by an important inorganic fraction, which are constituted by calcium carbonate and phosphate.
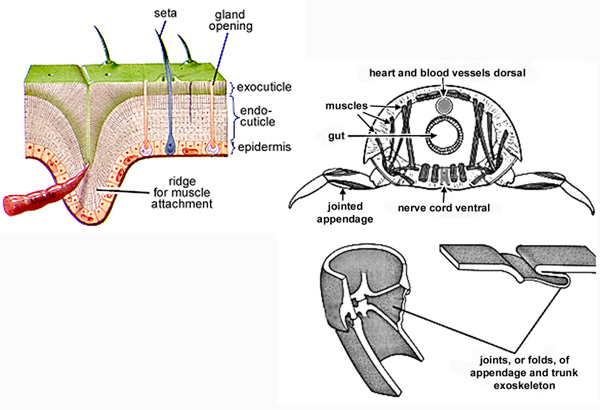
Source The arthropod cuticle and exoskeleton structure
As can be seen in the table on the following page, the edible crab contains the highest proportion of chitin.
Arthropod cuticles are abundantly available in many places in the world. The crabs or shrimps and their cuticles can be dried and chemically treated. Factories – for example in Scandinavian countries and Japan – for canning crab or shrimp meat daily discard a very large amount of chitinous raw material.
Chitin sediments in seawater were estimated to amount several billion tons per year, mostly due to moulted copepod exoskeletons. Therefore, Chitin is largely present in the ocean, for the shedded exoskeletons and dead bodies sink to the bottom.
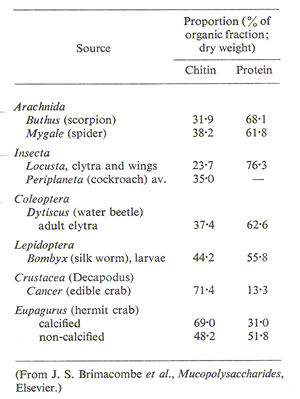
Source: Muzzarelli, R. A. A. : Natural chelating polymers
Is chitin harmful in someway?
Chitin is non toxic and biodegradable.
Chitosan
What is chitosan?
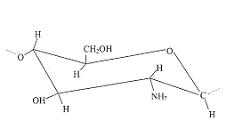
Chitosan is a polysaccharide created by deacetylating chitin (Deacetylatin: Removing acethyl groups (CH3CO)). Chitosan is biodegradable, non toxic and anti-bacterial. Chitosan can be used for many purposes in medical and industrial fields. The differences in chitosans are characterised by the viscosity, degree of deacetylation, % remaining proteins, solubility, transparency and turbidity.
Is chitosan harmful?
No (It's even used for medical purposes)
How do you produce chitosan from chitin?
Chemical methode: Chitosan is created from chitin by deacethylate chitin. First chitin is treated with hydrochloric acid (HCl) to dissolve the calcium, this is also called demineralization. To neutralize it, it is treaded with sodium hydroxide (NaOH), this chemical process is called deproteinization. Then the chitosan is dried and ready for use. Another method is with the use of enzymes known as chitin deacetylases. Chitosan created this way should be washed and dried first before use. Enzym methode: The chitin is deacetylated with chitin deactylase, which gives chitosan and acetate.
Is the production of chitosan from chitin harmful?
Both hydrochloric acid and sodium hydroxide are toxic when inhaled, swallowed or when contacted with skin and caustic. Both are harmul for the enviroment. Production with enzymes is less harmful.(of mss helemaal niet?)
What are the costs of chitosan production?
What are the possible applications of chitosan?
There are many usefull applications of chitosan. For instance, chitosan can be used for water treatment. Chitosan forms a combination with proteins, but in a way that recovery of proteins and chitosan is possible after use. This way chitosan can be used to remove metals from polluted water or it can be used for the clarification of wine, beer, juice etc. A membrane made out of chitosan can be used as a water softener. Chitosan can also be processed in paper. The paper will be antibacterial and extra solid so it can be used in the foodindustry as packing material. In this way, chitosan can also be processed in textile and even in food, all because off its antimicrobal quality. In the textile-industry chitosan is very popular because chitosan improves the textile qualities. Cotton becomes more crease-resistent and colours can be put on easier and stay visible longer. Chitosan can also be used for medical applications. It can be used as a bandage or as ointment for wounds, wich makes the wound heal faster and better (it helps to prevent scars). Chitosan has a mild affinity to human tissue. Therefore it can be used as artificial skin or as suture thread. Drugs- and cosmetics industry are also interested in chitosan for its capabilities as moisture retention. It can be used in cosmetics, for hair care or for skin care. Chitosan is often thougt to be able to combine to fat, therefore it is quite popular in dietary industry. But there is al lot of discussion about wether it works as a dietary product or not. Chitosan can also be used as oil in (industrial) machines.